6th Grade Skills, for some students are the final requirements of Elementary Math to master.
The 6th grade skills required in elementary math, are the same whether your student is still based in an elementary school, or has moved on to a middle school.
 |
Mastery of the sixth grade skills will give your kid an excellent foundation to start their further mathematics education. Once these are mastered they will be moving on to Advanced Mathematics - Algebra, Trigonometry, Euclidian Geometry, Calculus and Statistics. Ensure they know, understand and can apply all these skills in math - otherwise they will have trouble down the road. |
|
These Grade Level Expectations are organized by basic math subject area for 6th Grade, based on Washington States OSPI. If you would rather have a basic math skills requirements list organized by subject area, that includes every requirement from Kindergarten to 6th grade in one downloadable document please visit my Grade Level Expectations section. |
6th Grade Skills by Subject Area
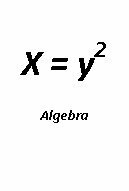 |
Algebra Exponents Review squares and square roots, using the terms squared and cubed and to the nth power, read and evaluate numerical expressions with exponents, review powers of ten, write numbers in expanded notations using exponents. Solve word problems with multiple steps Solve problems with more than one operation, according to order of operations (with and without a calculator) Recognize uses of variables and solve linear equations in one variable Solve word problems by assigning variables to unknown quantities, writing appropriate equations, and solving them Find the value for an expression, given replacement values for the variables, eg what is 7/x – y when x = 2 and y = 10? Simplify expressions with variables by combining like terms Understand the use of the distributive property in variable expressions such as 2x(2y + 3) |
 |
Numbers and Operations Read and write numbers (in digits and words) up to the trillions Recognize place value up to hundred-billions Integers (review) Locate positive and negative integers on a number line Compare integers using <, >, = Know that the sum of an integer and its opposite is 0 Add and subtract positive and negative integers Determine whether a number is a prime number or composite number Round to the nearest ten, nearest hundred, nearest thousand, nearest hundred thousand, nearest million Compare and order whole numbers, mixed numbers, fractions and decimals using the symbols <, >, = Determine the greatest common factor (GCF) of given numbers Determine the least common multiple (LCM) of given numbers Solve proportions including word problems involving proportions with one unknown Use ratios and proportions to interpret map scales and scale drawings Set up and solve proportions from similar triangles Understand the justification for solving proportions by cross-multiplication Convert between fractions, decimals and percent’s Find the given percent of a number, and find what percent a given number is of another number Solve problems involving percent increase and decrease Find an unknown number when a percent of the number is known Use expressions with percents greater that 100% and less and 1% Addition, commutative and associative properties: know the names and understand the properties Understand addition and subtraction as inverse operations Add and subtract with integers, fractions and decimals, both positive and negative Commutative, associative, and distributive properties: know the names and understand the properties. Multiply multi-digit factors, with and without a calculator Estimate a product Multiply with integers, fractions and decimals both positive and negative Distributive property for multiplication over addition or subtractions, that is A x (B +C) or A x (B + C) Understand multiplication and division as inverse operations Estimate the quotient Divide multi-digit dividends by up to three-digit divisors, with and without a calculator |
 |
Measurement Solve problems requiring conversion of units within the US customary system and within the metric system Associate prefixes used in metric system with quantities Kilo = thousand Hecto = hundred Deka = ten Deci = tenth Centi = hundredth Mili = thousandth Solve problems on elapsed time; express parts of an hour in fraction or decimal form. |
 |
Geometry Identify and measure the degrees in angles (review terms; right, acute, obtuse, straight) Bisect an angle Construct an angle congruent to a given angle Construct a figure congruent to a given figure, using reflection over a line of symmetry, and identify corresponding parts. Show how congruent plane figures can be made to correspond through reflection, rotation and translation Triangles Know that the sum of the measures of the angles of a triangle is 180’ Construct different kinds of triangles Know terms by which we classify kinds of triangles – length of sides, equilateral, isosceles, scalene – by angles, right, acute and obtuse Identify congruent angles and sides, and axes of symmetry, in parallelograms, rhombuses, rectangles and squares Find the area (A) and perimeter (P) of plane figures or given the area or perimeter find the missing dimension, using formulas of rectangle (A = lw; P = 2(l+w), square, (A = s2; P = 4s) triangle ( A = ½ bh; P = s1 + s2 + s3) parallelogram (A = bh P = 2(b + s) Circles Identify arc, cord, radius, and diameter; know that radius = ½ diameter. Using a compass, draw circles with a given diameter or radius. Solve problems involving application of the formulas for finding the circumference of a circle: using 3.14 as the value of Pi Find the volume of a rectangular solids or given the volume find a missing dimension, using the formulas V = lwh or V = bh (in which b = area of base)
|
 |
Data Analysis Find the range and measures of central tendency (mean, median and mode) of a given set of numbers. Understand the use of a sample to estimate a population parameter (such as the mean) and that larger samples provide more stable estimates. Represent all possible outcomes of independent compound events in an organized way and determine the theoretical probability of each outcome. Compute the probability of any one of a set of disjoint events as the sum of their individual probabilities. Solve problems requiring interpretation and application of graphically displayed data. Construct a histogram; a tree diagram. |
Other Sections of this site
Keep In Touch!
You can send me a quick message, follow me on Facebook or why not join our community of like minded parents? Choose all the options so you don't miss any of the new material added to this site.











